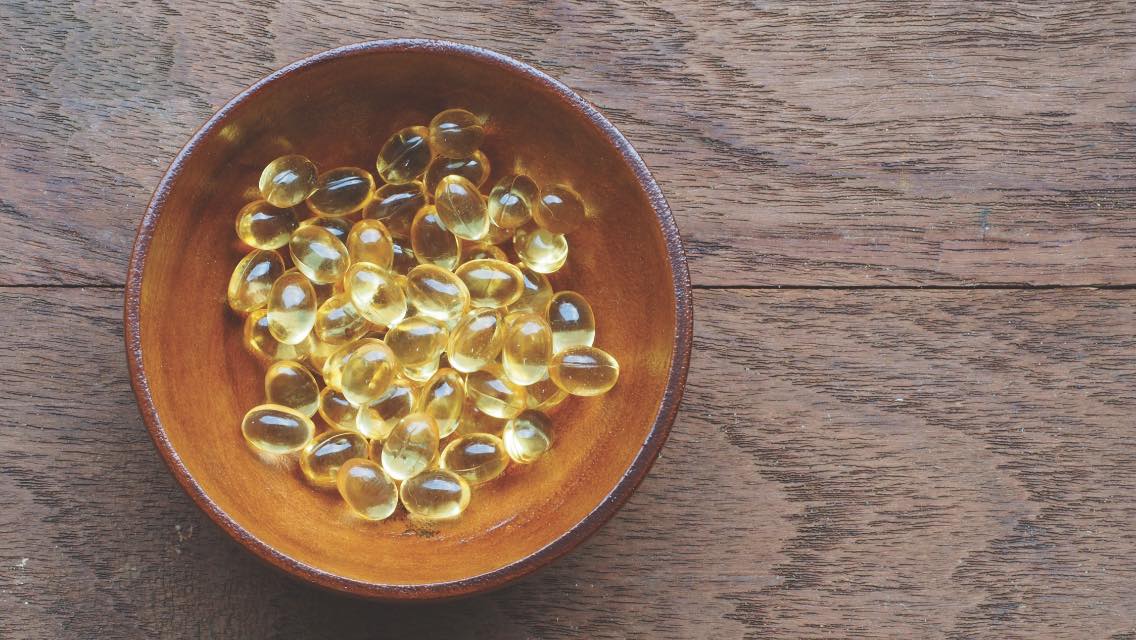
Along with omega-6 fatty acids, omega-3s (which are found in fish oil) are part of a special group of fats called essential fatty acids. Like essential amino acids, essential fatty acids are nutrients you need in your diet because your body can’t make them on its own.
Most don’t need to give much thought to eating enough omega-6s as they’re prevalent in the diet — and consuming too much at levels out of balance with omega-3s can be problematic. Omega-3s, however, are challenging to consume enough of through food alone.
Although plant foods like flaxseeds, walnuts, soybean, and wheat germ contain a pretty decent amount of omega-3s, the omega-3 fatty acid found in these plants is called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is not the ideal type for humans as we don’t easily convert ALA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Fatty fish is the direct food source for consuming EPA and DHA. And most of us are not eating enough to create a healthy balance of omega-6s and omega-3s. There is also a risk of consuming too much mercury if you overeat fatty fish.
This is why a high-quality fish oil is beneficial: It can provide your body with EPA and DHA and it is filtered to virtually eliminate mercury.
Supplementing with fish oil can be so advantageous that it’s included in our Foundational Five, which is our bundle of the daily supplements that we recommend for most everyone.
What Are The Benefits of Fish Oil?
Fish oil is often known for its heart health benefits, but its impact can also provide so much more than that.
1. Enhances Fat Loss
Animal research shows that fish oil consumption causes fat loss by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system, which releases noradrenaline. Noradrenaline stimulates brown adipose tissue, raising metabolic rate and heat production. The researchers used high-EPA fish oil at doses of up to 2.4 percent of the animals’ total calorie intake. For an adult on a 2,000-calorie diet, that would equate to about 5 grams of fish oil per day.
Fish oil seems to be especially useful for reducing visceral or belly fat. Some studies show that fish oil supplementation doesn’t affect body weight, yet it still helps reduce waist-to-hip ratio and visceral fat. In these studies, it’s likely that the fish oil also increased lean body mass while reducing body fat. The scale might not change significantly, but body composition and health risks improve.
A small 2010 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found the following:
Forty-four men and women supplemented with either four grams of safflower oil or four grams of fish oil. Those taking the fish oil decreased body fat and body fat percentage, increased lean body mass, and experienced a decrease in cortisol levels. Interestingly, the study participants were not instructed on diet or exercise. They were encouraged to keep their nutrition and exercise patterns the same as before the study.
Noreen, et al. 2010
Another reason fish oil helps with fat loss is that it causes fuel partitioning. The omega-3s help your body store more calories as glycogen (stored carbohydrate) rather than as fat. Fish oil can also help improve satiety.
2. Supports Healthy Lipids and Blood Glucose
Though your doctor probably still focuses their attention on your total and LDL cholesterol levels, the more important numbers are your triglycerides and HDL.
| TRIGLYCERIDE/HDL RATIO | |
|---|---|
| Ratio | Risk Level |
| 1:1 or Less | Optimal |
| 2:1 | Low Risk |
| 3:1 | Moderate Risk |
| 4:1 | High Risk |
Supplementing with omega-3s has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, lower triglycerides, and in some studies, improve HDL cholesterol levels.
Blood glucose and triglycerides go hand in hand, as you need glucose to build triglycerides. The more sugar in your diet, the higher your triglyceride levels rise. So, it’s no surprise that fish oil supplementation, which has consistently been shown to support normal triglyceride levels, also promotes healthy blood-sugar levels and better insulin sensitivity.
Between EPA and DHA, it’s EPA that seems to affect triglycerides the most. And it’s been shown to be effective in adults as well as children.
Fish oil supplementation was also shown to lower lipids and glucose in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
3. Increases Lean Body Mass and Strength
Research on all types of people shows that the addition of fish oil to the diet can enhance strength and increase lean body mass. In older adults, it can also slow the loss of lean body mass, making it a great complement to a high-protein diet, amino acid supplementation, and other muscle-building supplements.
Of the two most important omega-3s, DHA and EPA, it appears EPA has the most significant effect on protein synthesis. In research, it was shown that protein synthesis increased by 30 percent when fish oil was combined with a sufficient amount of protein or amino acids, compared to amino acids or protein alone.
Muscle growth is a result of increased protein synthesis and/or decreased protein breakdown. The regulation of protein breakdown is controlled by a different process than protein synthesis, and evidence shows that EPA affects both sides of the equation.
4. Supports Healthy Inflammation Levels and Immune Function
Chronic inflammation is considered one of the leading causes of heart disease. Fish oil protects the heart by supporting healthy levels of inflammation.
In a study that used human blood samples, EPA+DHA intake changed the expression of 1040 genes and resulted in a decreased expression of genes involved in inflammatory and atherogenesis-related pathways.”
Bouwens M, et al. 2009
Fish oil supplementation can be especially helpful for those who endurance train or do a lot of cardio exercise as they’re more likely to experience inflammation. Inflammation is an immune response, and fish oil not only helps support normal inflammatory levels, but it’s also been shown to support the function of white blood cells.
The endocannabinoid system regulates inflammation. DHA and EPA can be metabolized into cannabinoids, making these omega-3s important for the function of your endocannabinoid system.
5. Improves Nutrient Delivery To Cells
Higher intake of omega-3s can change the composition of the cell membrane, allowing nutrients to flow in and out easier. The percentage of omega-3s in the cell membrane can easily be measured through a finger stick blood test.
Not only does fish oil help with nutrient delivery to the cell, but a multivitamin may also improve the assimilation of omega-3s into the cell membrane: Taking a multivitamin along with fish oil improved the red blood cell’s ability to take up omega-3s into the cell membrane.
Just another example of why the first two supplements recommended by Life Time experts are a high-quality multivitamin and fish oil.
6. Supports Brain Function
DHA is crucial for brain development in the womb. Many studies show large differences in later development when comparing babies born from mothers who supplemented with fish oil and those who did not. For example, at 2.5 years after birth, toddlers of mothers who supplemented with fish oil had significantly improved hand and eye coordination compared to toddlers of mothers who did not supplement.
And the effect of DHA on brain health continues throughout life. Some research indicates DHA could ward off or slow the effects of Alzheimer’s and other cognitive diseases.
7. Additional Benefits
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, fish oil supplementation may:
- Reduce psychological distress
- Reduce some symptoms of depression
- Enhance eye health
- Improve skin health
- Possibly reduce the occurrence of infant allergies if used during pregnancy
- Possibly reduce chest pain (acute coronary syndrome)
- Reduce age-related sight loss
How Much Fish Oil Should You Eat or Take?
Most of the research showing the benefits mentioned above have participants taking 1 to 2 grams of EPA/DHA per day, or two to six fish oil soft gels. Conservative recommendations for daily DHA and EPA intake range from 1 to 4 grams. Omega-3 soft gels vary in their DHA and EPA content, but the label will show you how much is in there.
Lower-quality fish-oil supplements usually have about 300 mg of EPA and DHA combinedper one-gram softgel, while higher quality softgels have around 500 to 600 mg. The LTH Glow Omega-3 Fish Oil supplement contains 360 mg EPA and 240 mg DHA per softgel for a total of 600 mg.
A typical salmon steak provides about one gram of EPA and DHA. Of course, most people do not eat fatty fish every day, which makes supplementation important.