A research team led by John Porcari, PhD, and Chad Schnettler, MS, at the University of Wisconsin–La Crosse Exercise and Health Program studied the effects of a specific kettlebell routine on 10 volunteers, male and female, ages 29 to 46 years, all of whom were experienced with kettlebell training. Following fitness testing to assess their baseline cardiovascular conditioning, the subjects performed an intense 20-minute series of kettlebell snatches (a whole-body exercise performed in an interval-training format) while having their heart rate and oxygen consumption monitored, and their blood lactate levels taken after the workout.
The results?
An average burn of 20.2 calories per minute (equivalent to 1,200 per hour), which Porcari characterized as “off the charts” — and average heart rates at 93 percent of max. The researchers’ conclusion: High-intensity kettlebell training can trigger positive changes in aerobic capacity and muscular development while simultaneously supporting fat loss, allowing exercisers to accomplish more in less time. Read about the study at www.acefitness.org/getfit/research.aspx.


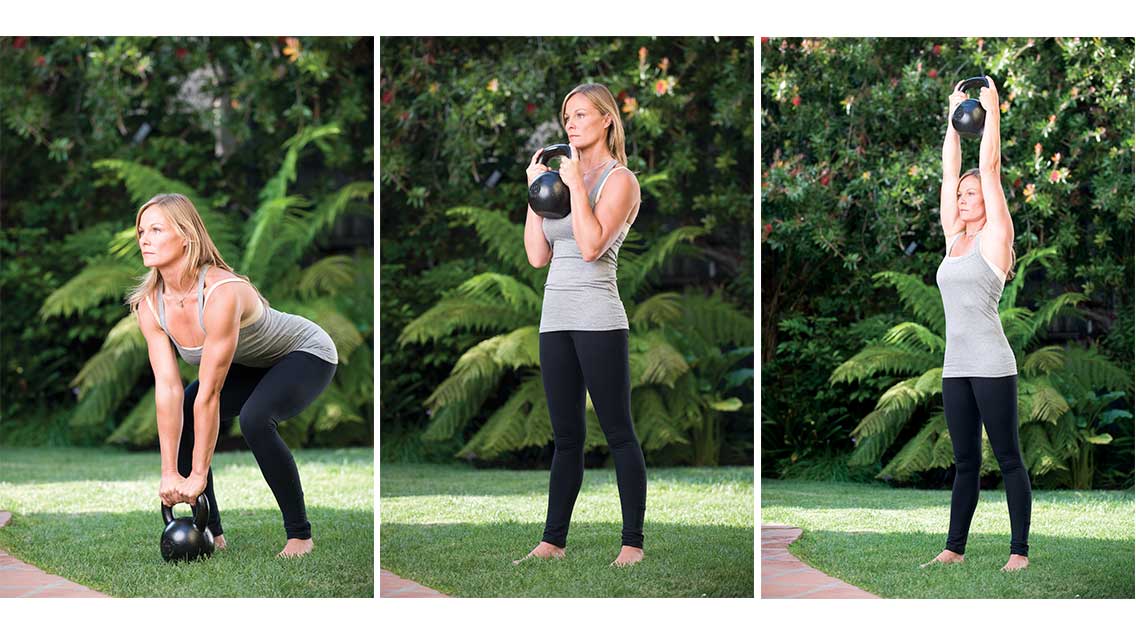
This Post Has 0 Comments